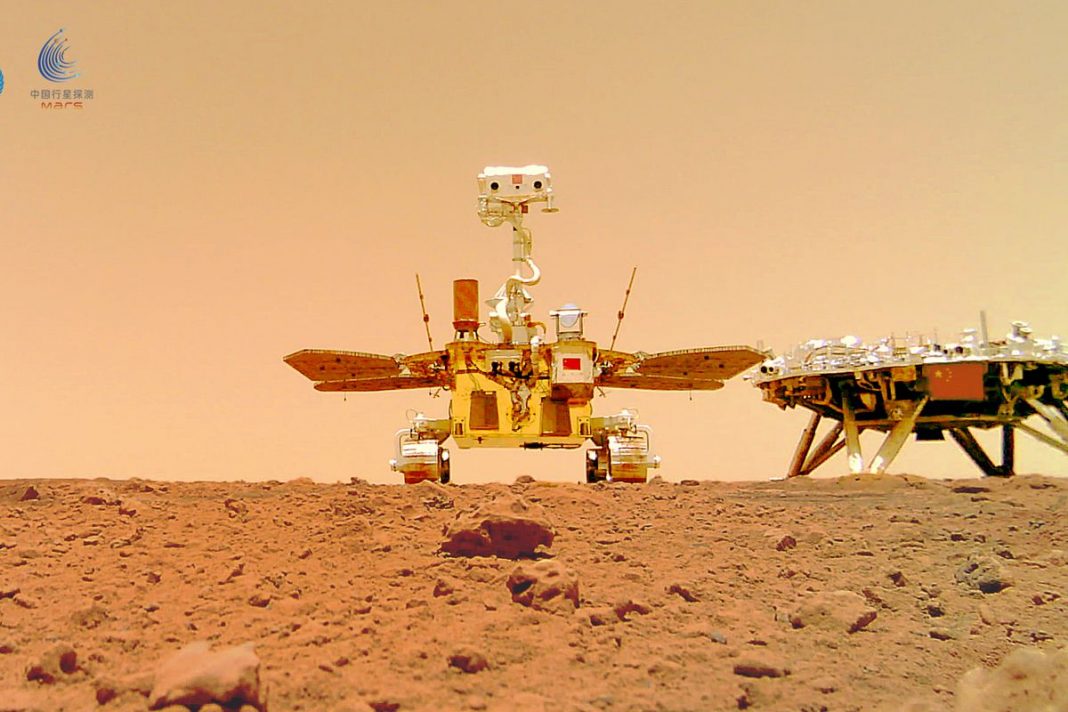
Working on Mars Chinese Chu-jung rover found traces of erosion caused by water and wind.
The Nature Geoscience a recent study published in the journal of the International Journal of Science and Technology, analysed data collected during the first 60 days of the first 60 Mars missions of the Chinese Mars rover Chu Jung, named after a fire goddess of ancient Chinese mythology. During this time, the rover travelled 450 metres around the red planet.
A team of researchers from China's Harbin University of Technology studied the rocks on Mars using data collected by the structure's camera, and found that the Martian soil has a cohesion that suggests wind erosion. The researchers suggest that the ridges and undulating surfaces seen in the images may once have been ravaged by wind.
However, this is not the only important finding: in addition to wind erosion, the researchers also found evidence of water erosion, which suggests that the area was salt water.
The Chu-jung is a 1.85-metre-tall, 240-kilogram Mars rover, which was built by the Tienven-1 guided by a probe. The rover's mission will include studying the Martian atmosphere and soil, taking images and mapping the plains of Utopia Planitia. In Chinese mythology, Chu-jung was the god of fire, the body of a beast, the face of a man and rode two dragons.
Although Chinese space exploration is developing at a rapid pace, relatively little information about their missions is shared with the world, and only limited information about their launches and spacecraft is released.







![[148] HyperOS heti hibajelentés](https://helloxiaomi.hu/wp-content/uploads/2024/04/hyperosbugreport148-218x150.webp)


![[42. Hét] HyperOS globál ROM változások](https://helloxiaomi.hu/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/hyperoschangelogindex1080-218x150.webp)
![[40. Hét] HyperOS globál ROM változások](https://helloxiaomi.hu/wp-content/uploads/2024/03/hyperoschangelogindex-218x150.webp)